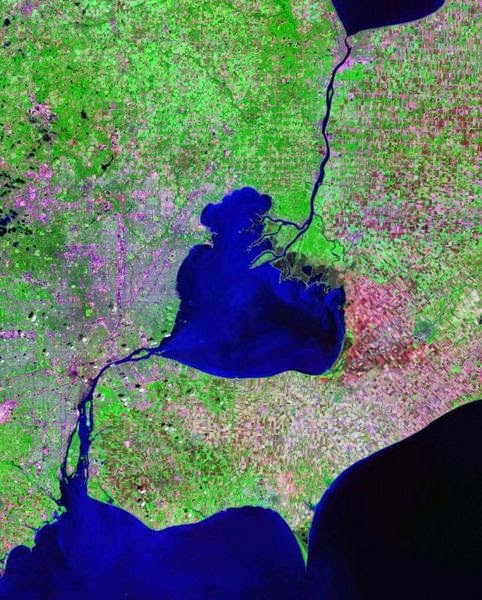
The St. Clair River is a 40.5-mile-long (65.2 km) river in central North America which drains Lake Huron into Lake St Clair, forming part of the international boundary between the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. state of Michigan. The river is a significant component in the Great Lakes Waterway, with shipping channels permitting cargo vessels to travel between the upper and lower Great Lakes.
Location
The river, which some consider a “strait,” flows in a southerly direction, connecting the southern end of Lake Huron to the northern end of Lake St. Clair. It branches into several channels near its mouth at Lake St. Clair, creating a broad delta region known as the St. Clair Flats.
Size
The river is 40.5 miles (65.2 km) long and drops 5 feet (2 m) in elevation from Lake Huron to Lake St. Clair. The flow rate averages around 182,000 cubic feet per second (5,200 m3/s), and the drainage area is 223,600 square miles (579,000 km2). This takes into account the combined drainage areas of Lakes Huron, Michigan, and Superior.
Erosion and Great Lakes Drainage
Federal officials have long acknowledged that dredging and riverbed mining in the St. Clair dropped the long-term average of Great Lakes Huron and Michigan by about 16 inches. A bi-national Great Lakes water-level study concluded in 2013 that unexpected erosion since the last major St. Clair dredging project in the early 1960s has dropped the lakes’ long-term average by an additional 3 to 5 inches. Today, these lakes are nearly 2 feet lower than before human modifications to the riverbed of the St. Clair River. This record low has raised concerns about the long-term health of the lakes. Activists urge remediation to slow the flow of waters through the St. Clair River and out of the lake system, to restore former water levels.
Note : The above story is based on materials provided by Wikipedia










